Table Of Content

However, this hierarchy is quite subtle, creating a level of visual tension (and reflecting, perhaps, the tension in the conversation). Visual hierarchy isn’t an exact science, particularly in more complex layouts. Someone’s attention can usually be directed to the first and second areas of focus, but after that, their visual journey can get less predictable. Visual hierarchy is about the relative visual prominence of different elements in a layout. These principles have remained largely unchanged for hundreds, if not thousands, of years. That’s because visual principles aren’t about aesthetics — they’re about how people see, and how we interpret visual information.
Why is it important to master advanced design principles like contrast and unity?
For instance, in a website design, a prominent call-to-action button with a vibrant color can attract the user's attention and prompt them to take action. In visual design, mastering emphasis is crucial for effective communication and creating memorable designs. Designers should aim to understand how each of these design principles actually impact their work.
Texture
Here, scale is your best friend to ensure that your content doesn’t just fit, but also shines, regardless of screen size. Our first click testing on Unanet’s site revealed that their Request a Demo button in the hero dominates the visual hierarchy, with over 66% of participants clicking there first. I like to use these principles when making something usable but still beautiful. White space doesn’t necessarily have to be completely white or free of pattern. In fact, subtle patterns can add visual interest to white space while still allowing it to function as a sort of visual “breathing space” within a design.
Putting visual design elements and principles into practice
Anti-Design Is Intentionally Loud and Messy - Built In
Anti-Design Is Intentionally Loud and Messy.
Posted: Mon, 08 Apr 2024 19:21:04 GMT [source]
It’s not just about throwing content on the page and hoping it sticks. Nope, it’s about arranging it all so that users can take one glance and instantly understand what’s going on. In the film scene, there is asymmetrical balance between the two main areas in the visual hierarchy. Contrast is about combining different sizes, colours, and styles to support visual structure, and often to create visual drama. Spacing in design is similar to the spaces between notes, phrases, and movements in classical music.

In addition, there are another dozen or so “secondary” design principles that are sometimes included as basics (for example, the Gestalt Principles, typography, color, and framing). The main design principles are explained and illustrated below. Hierarchy in design refers to the arrangement of elements in a way that signifies importance. It guides viewers' eyes, ensuring they focus on primary information first, followed by secondary and tertiary details. Designers establish a visual hierarchy by employing size, contrast, color, and spacing, directing attention and aiding comprehension.
What are the elements of visual design?
Pattern also helps differentiate things, and color and contrast make things stand out and blend in. In this simplistic yet elegant design, a contrast in colors adds depth of field and distance between objects. It provides breathing room between other design elements to highlight spaciousness. Negative space is a big component in web and graphic design, creating a feeling of minimalism and simplicity.
For instance, if the flowers were faded and turning brown and the robot was dull and rusted. But instead, the bright colors help paint a scene that is innocent and welcoming. Even though most of the shapes here are symmetrical, we can still see some asymmetrical shapes, such as the birds, but are still classed as shapes. This article will aim to eliminate the blur between both these closely related terms to help you understand how AI and ML are tied to data science...
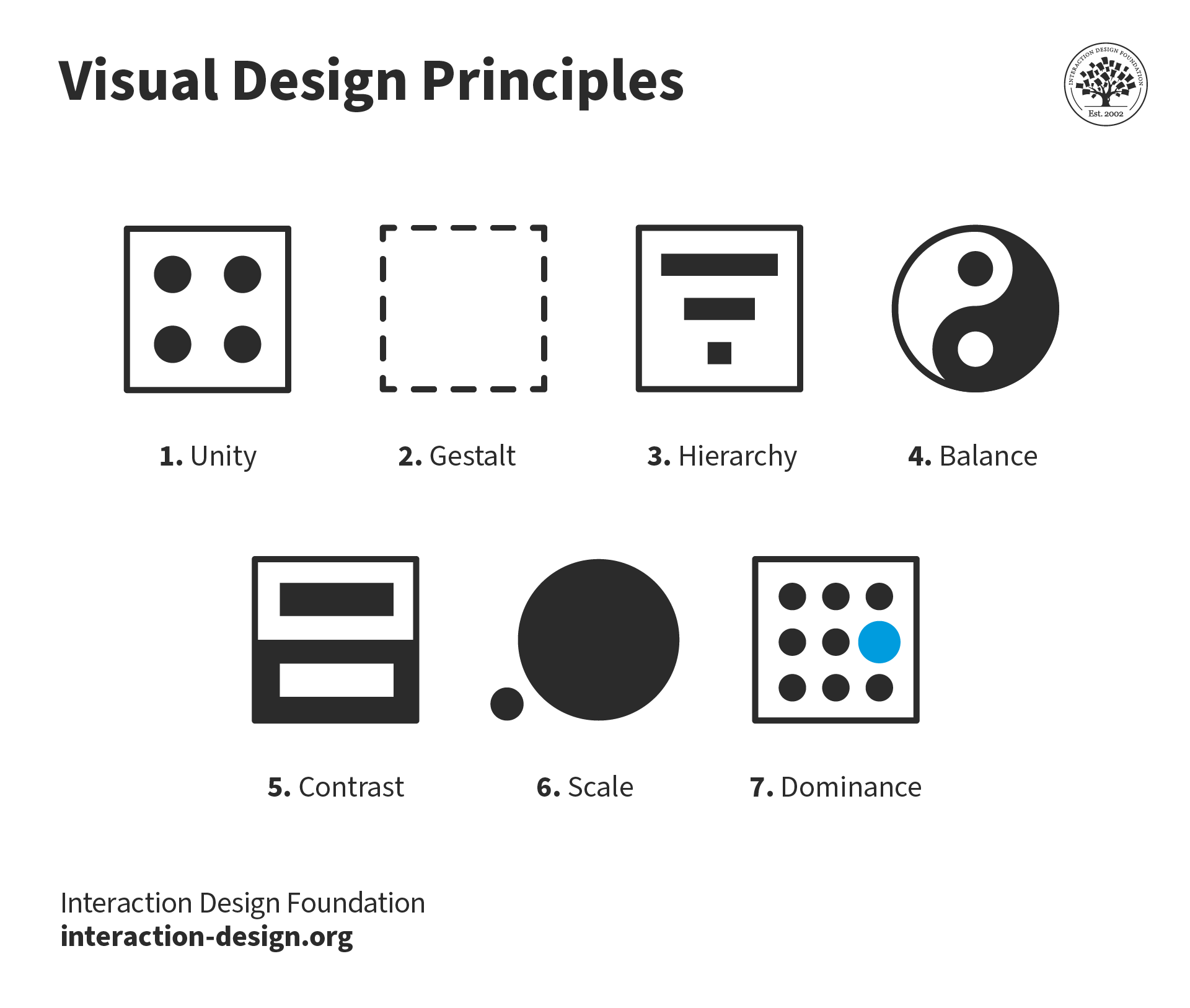
visual hierarchy principles for web design
The texture used in this example fits well with the brand's natural and tactile essence. Website wireframes are a great example of how mechanical shapes are used in visual design. As shown in this example by Adam Kalin, wireframes contain clearly defined rectangles and circles.
Understanding how these elements interact and influence each other is vital for mastering visual design and producing exceptional results. By manipulating these elements purposefully, designers can convey specific emotions, messages, and aesthetics in their designs. White space, also known as negative space, refers to the empty areas within a design. It is equally important as the elements themselves, as it provides breathing room, clarity, and visual balance. For example, a black and white photograph with a single red flower can create a striking contrast that draws the viewer's attention to the flower.
Visual design isn't just a supplementary skill for instructional designers; it's a powerful tool in the arsenal. By intertwining effective visuals with solid content, we can craft experiences that are memorable, engaging, and impactful. It's when every design element and principle comes together as one, creating harmonious flow and tranquility.
Therefore, follow this principle of design to execute outstanding ideas. When you take part in this course, you’ll join a global community and work together to improve your skills and career opportunities. Connect with helpful peers and make friends with like-minded individuals as you push deeper into the exciting and booming industry of creativity and design. You will have the opportunity to share ideas, learn from your fellow course participants and enjoy the social aspects afforded by our open and friendly forum. For example having CTA, image, and introductory paragraph placed on the Home screen are related to each other by the context. Where the image and paragraph tell about the website and CTA is there to lead an activity.
The principle of invariance states that your brain is skilled at pinpointing similarities and differences. That’s why it's really easy to make something stand out in a crowd of similar objects. So, when your brain is digesting an image and trying to make sense of it, first, it will take stock of the outline.
Differences in values create clear designs, while designs using similar values tend to look subtle. Although simple, lines can possess a large variety of properties that allow us to convey a range of expressions. Design is a complicated business full of principles, tricks, and techniques, some of which you can learn from others, and some of which you must learn on your own. Unity can also reveal symbolism to the viewer, creating a subjective experience that is unique to the viewer. This painting of these flowers is a perfect example of symmetrical balance, where everything is a mirror reflection from left to right.
Repetition generally creates unity in a design without any extra effort on the part of the designer. But used intentionally, it can take that unity to a higher level. The subtle grid pattern in the background of this design adds some visual interest without being overwhelming to the eye. Proportion refers to the relationship between different elements within a design. It involves the size, scale, and dimensions of various components in relation to each other and the overall composition. Grid and alignment are closely related to balance and refer to the way elements are arranged in relation to an invisible grid on the page.
Ideally, this should be the most important part of the design, whether that’s the headline, an image, or a CTA. Alignment refers to how text or graphic elements are lined up on a page. This can refer to their alignment in relation to the entire composition (left, center, or right-aligned) as well as their alignment to one another. Whichever type of balance technique you use, the result should feel right. It should give the viewer a sense of harmony and not make them feel uneasy.
Learn 11 core principles of design and how to apply them to your graphic design work. Some designs make use of negative space to create interesting visual effects. For example, the famous World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) logo makes use of the confusion between positive shape and negative space to create the image of a panda.